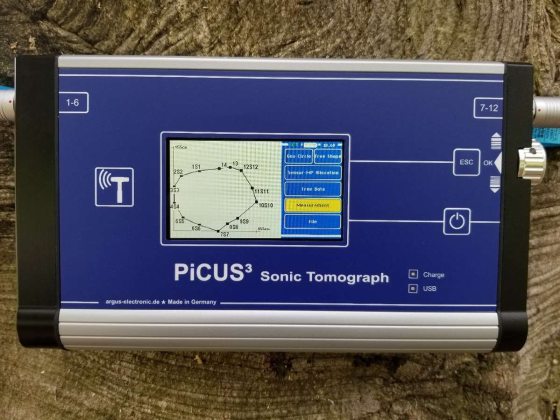
At Longwood, the health and care of our trees has always been of utmost importance—after all, Longwood came to be after founder Pierre du Pont purchased the land in 1906 to preserve its trees and we continue to go to great lengths when it comes to our multi-faceted, peer-reviewed Tree Management Plan. In the last year, we have started to use a PiCUS Sonic Tomograph, a device that uses sound wave technology to advance tree care and the accuracy of tree risk assessments by allowing arborists to get a look at the inside of the tree when assessing its structural integrity. Our PiCUS device is just one of the many tools in our tree care toolbox, which includes annual visual inspections with risk assessments; industry standard pruning protocols; lightning protection methods; climate change modeling; and our Specimen Tree Replacement Plan, which preserves the genetics of select trees in our Gardens, among other facets. We are thrilled to have this technology at our fingertips, as it has quickly become an integral component of our tree care program here at Longwood.
The device can be intimidating and complicated in use, but the concept of how it works is simple—not unlike knocking on drywall to find a stud. In its simplest form, the PiCUS device measures the velocity of sound waves through the cross-section of a tree to extrapolate the structural integrity of the wood within. Sound travels quickly through solid (or healthy) wood but slowly through soft (decaying) or nonexistent wood (hollow).

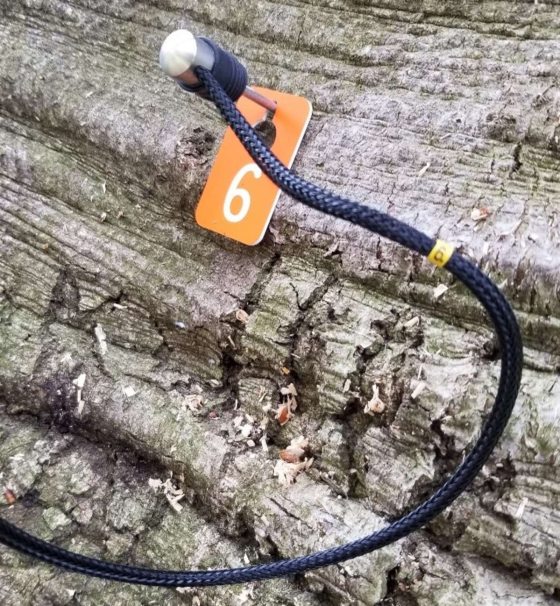
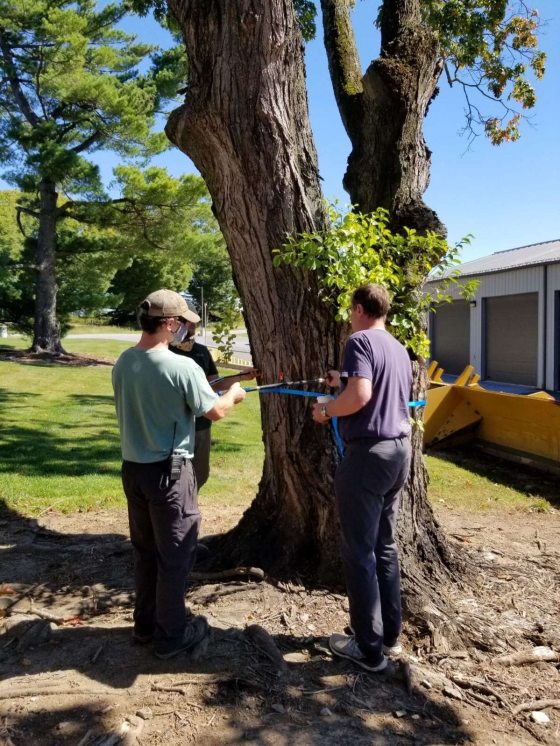
The process begins by measuring the diameter of the cross section that is going to be scanned. Pins are then installed through the bark, and just into the wood of the tree. The pins are placed 10 to 20 centimeters apart around the circumference of the tree. Depending on the tree or limb’s diameter, anywhere from eight to 24 or more pins may be used. These pins are referred to as measuring points, or MPs. Next, the tree’s shape needs to be calculated. If the tree is nearly perfectly round, the software can use its “geometric circle” function to calculate the shape and spacing between MPs by the using the diameter. If the cross-section is irregular, such as around the root flare of the tree, electronic measuring calipers are used so the exact shape can be captured, as seen above.

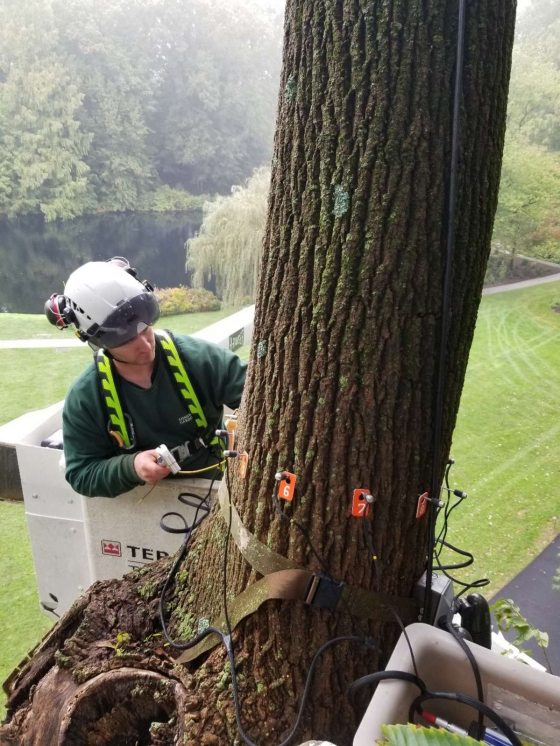
Once the shape is set, the scanning can begin. Longwood’s unit has 12 sensors, which are placed on the MPs. If there are less than 12 MPs, then that number of sensors is used. If there are more, there will be a second stage when the sensors are reallocated past MP12, and scanned again. A special hammer is used to tap on the MPs while the device software captures all the data. This step is called tapping and represents how the device got its name, as Picus is Latin for “woodpecker”. Once all the tapping is complete, the device will share a preliminary image only using a few colors. Once the file is uploaded into the computer-based software, a more accurate image is created based off the tree’s condition. Different colors mean differing wood qualities. Brown means sound waves are traveling well, suggesting the wood is structurally sound. Green is a transition between live wood and decay, while yellow, blue, and white means sound waves are traveling slowly or taking longer to transverse decay or a hollow.

According to Urban Forest Innovation Solutions (UFIS), a Toronto-based distributor of specialized tree care devices, only 50 such PiCUS units exist in the United States. Longwood purchased a PiCUS device in 2020, and were scheduled to have staff from UFIS travel here to conduct a hands-on training session, until the COVID-19 pandemic began. After numerous, at-length phone calls, virtual training and, finally, a hands-on course, Longwood arborists started actively using the device in early 2021 to provide highly accurate assessments of the structural integrity of trees. This tool will complement our IML Resistograph, which is a device that uses a small diameter drill bit to drill into the tree and measure the resistance of the wood. Simple, two-dimensional diagrams can be created afterwards.

This minimally invasive method helps our arborists get a good idea of what the structural integrity of the tree is, functioning almost like an x-ray. Not only do we get an idea of what the inside of the tree looks like but, using the coloring, we can assess how the wood is reacting to decay or other stressors.
The Longwood arborists have already used this device to aid in the completion of a tree risk assessment of a tree with signs of internal decay near old pruning cuts at about 40 feet. We used the PiCUS device in the area with suspected decay, noting that areas of dead bark could be heard when knocked on, from this point down to the northern root flare.
While inspecting this potentially dead area of sapwood, we noticed some small decay at the base of the root flare and decided to do a quick scan two feet off the ground. As a result, we noticed two things. One was that the visible decay at 40 feet did not extend very far into the tree, so this was no longer a concern. Second, the lower trunk scan showed a small pocket of weakened wood in the center of the tree (seen as a green spot in the far right photo below). One very important thing to know about root rot or buttress flare decay is that it is typically pyramidal in form. This means that below ground or in the roots, extensive decay can exist but can then taper up to solid wood only a few feet up. Therefore, root rot and buttress flare decay has the potential to present a high level of risk because this is where the most amount of leverage is on a tree, making it very important to inspect on trees with known buttress defects.
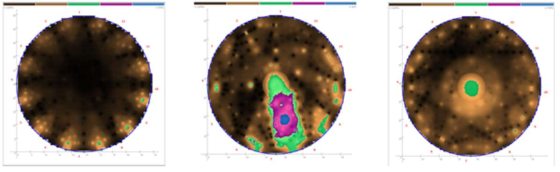
Knowing this, the next day we did an additional scan only a few inches above grade (1.5 feet lower than the initial scan) and found a significant amount of decay around the soil line, which is a common characteristic of trees that have had root damage. Decay works its way up the tree but as the tree’s internal mechanisms fight it off, it tapers to little or nothing. Once we analyzed the final tomogram on a computer, we made the recommendation for removal in the near future (the tree grew straight, had a small relative canopy size, and had already lost its leaves in the fall, so there was not an immediate risk of failure). Following review by our Longwood team, it was cleared for removal. When the tree was removed, we were able to get a real-life look at the inside of the tree and saw firsthand just how extremely accurate the PiCUS device had read. There was, in fact, significant decay along with possible cracks forming along the root flare of the tree, as seen below.
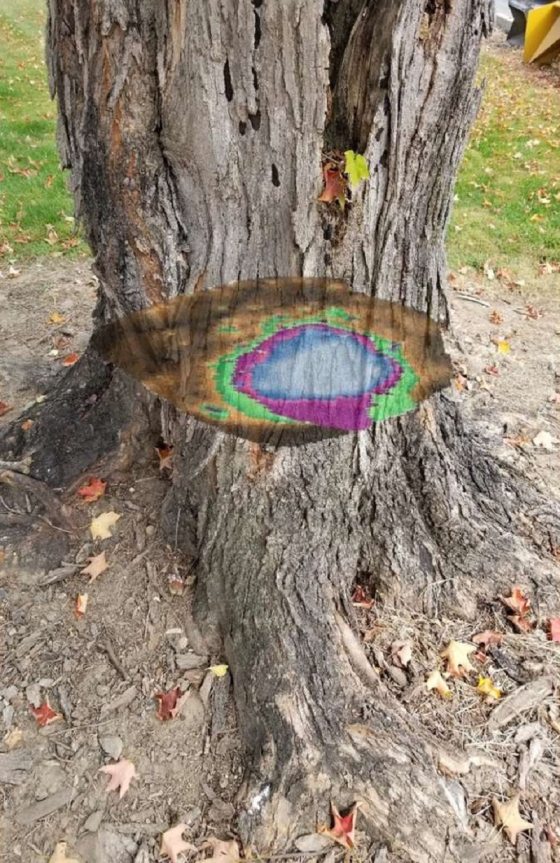
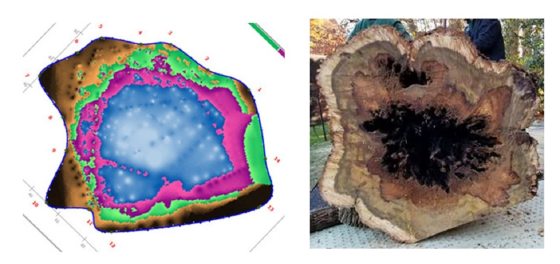

The PiCUS device can help us confirm or deny educated guesses about our trees and serves as a cutting-edge addition to our tree care toolbox. The purpose of the device is not to push for tree removals but instead to help educate our arborists on what we cannot see. We look forward to using our new tool-in-the-toolbox to continue to gather more accurate data on the health of our mature trees, all in hopes of retaining trees longer and making certain that tree removals occur only when absolutely necessary.


